The United States Healthcare system has experienced challenges for decades now. Despite efforts taken by the U.S. to improve the problems in healthcare over the last decade, most individuals believe that it has a host of issues in need of repair.
According to a study by Public Agenda, only 7% of Americans are satisfied with the current healthcare system. 6 out of 10 people, despite political affiliation, believe the system needs changes or a complete overhaul.
To improve healthcare in America, we must understand the challenges it faces this year. Here are five challenges facing healthcare in 2023:
1. High Costs of Healthcare
In comparing the median prices paid by private health insurance companies for specific services among nine countries, The Health Care Cost Institute found costs for healthcare were substantially more in the U.S. than the other countries. Healthcare costs increased due to staffing shortages, supply change problems, and rising inflation rates.

Here are some statistics that demonstrate the increasing costs of healthcare:
- The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services and the Office of the Actuary predict that national healthcare spending in the U.S., which reached 3.81 trillion dollars in 2019, will reach $6.19 trillion in 2028 and account for 19.7% of the GDP.
- The Health Cost Institute reports that in 2021, for those with insurance coverage through an employer, the per-person spending rose to $6,467 from $5,630 in 2020.
- In the same report from The Health Cost Institute, per-person healthcare spending increased by 15% in 2021. The average prices also increased by 2%, making it 14% higher in 2021 than in 2017
- According to Regis College, more than 45% of American adults say it is difficult to afford healthcare. ¼ th of Americans cannot afford prescriptions.
- According to a survey by The Kaiser Family Foundation, more than 40% of Americans have medical debt.
- About 60% of households earning less than $100,000 report witnessing or experiencing severe financial stress due to healthcare costs.
High medical costs directly impact public health. As people experience high medical costs, their behavior can change. It can cause missed prescription doses, avoiding doctor visits when ill, and avoiding preventative care visits.
Patients avoiding healthcare spending can lead to serious long-term health issues and ultimately increase individual costs.
Why is a Kudoboard a great way to say thank you? ❤️ It’s a thoughtful and heartfelt way to show a healthcare worker how much they’re appreciated!
Learn about healthcare recognition
2. Improving Health Equity
In recent years, organizations, healthcare professionals, and lawmakers have made an increased effort to improve health equity. However, organizations still need much improvement in health equity.
Health equity is achieved “when all people, regardless of race, sex, sexual orientation, disability, socio-economic status, geographic location, or other societal constructs have fair and just access, opportunity and resources to achieve their highest potential for health (Health Equity Tracker).”
Many social and political factors negatively impact many communities’ ability to live healthy lives. These factors are known as social determinants of health and are:
- Zip code
- Race and ethnicity
- Air and water quality
- Access to jobs, housing, education, transportation, and nutritious food
- Lack of education
- Socio-economic status
The vast disparities in healthcare outcomes significantly impact patients within the healthcare system. These patients’ long-term health is harmed without proper educational materials, access to non-biased healthcare, or environmental factors influencing quality care.
For example, Deloitte reports that Black patients are 2.5 times more likely to have their behavior and history negatively characterized in Electronic Health Records (EHR) notes than White patients. Black adults are also 60% more likely to be diagnosed with diabetes and two or three times more likely to have complications. The increased complications may be because racial inequalities often contribute to late diagnosis and other comorbidities that lead to more complications.
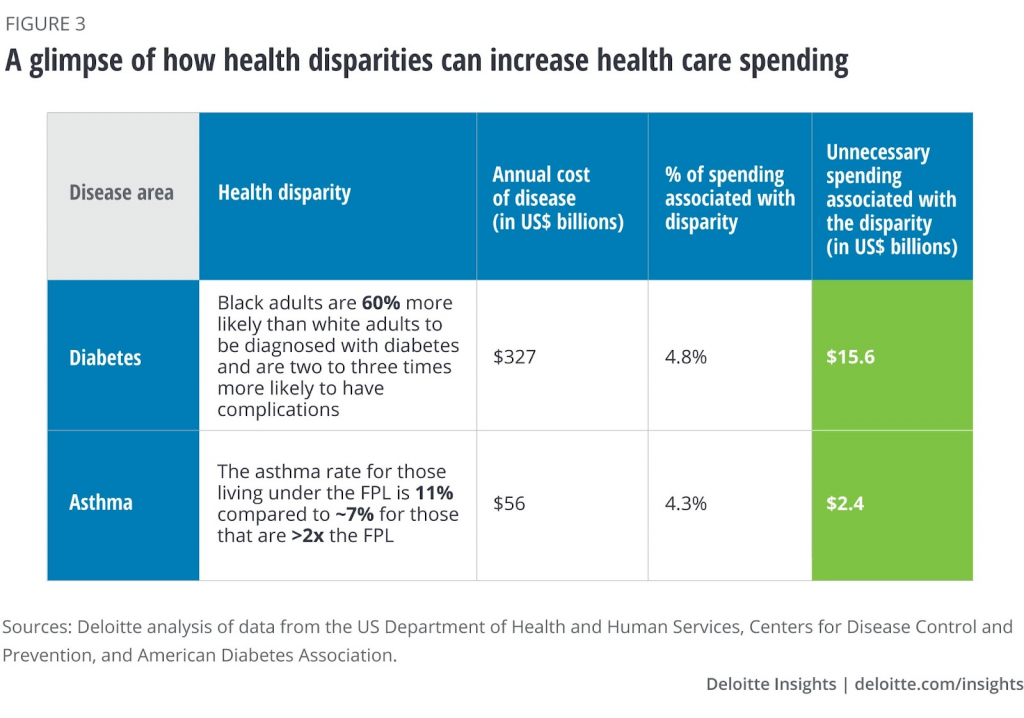
Racial and Ethnic minorities and those with less education and low income are more likely to be uninsured. Lack of insurance will increase individual costs and further disparities in health equity.
Deloitte Magazine also reports that Healthcare inequities account for nearly $320 billion in annual spending. This number could rise to $1 trillion by 2040.
Pierre Theodore, M.D. and vice president of health disparities at Johnson & Johnson Global Public Health explained, “The underlying problem of health care spending is health inequity….When you address inequities for one population, you raise health for all populations.”
3. Lack of Insurance Coverage
Directly linked to the challenge of increasing medical costs is the amount of individuals who do not currently have insurance coverage.
About 30 million people in the United States do not have health insurance. Because those without insurance are less likely to seek preventative care and necessary health screenings, they are more likely to have poor health outcomes.
These poor health outcomes lead to greater suffering and, ultimately, higher costs to the individual. According to The Institute of Medicine, “primary clinical preventative services have an estimated net savings of $7 billion.”
4. Quality of Patient Care
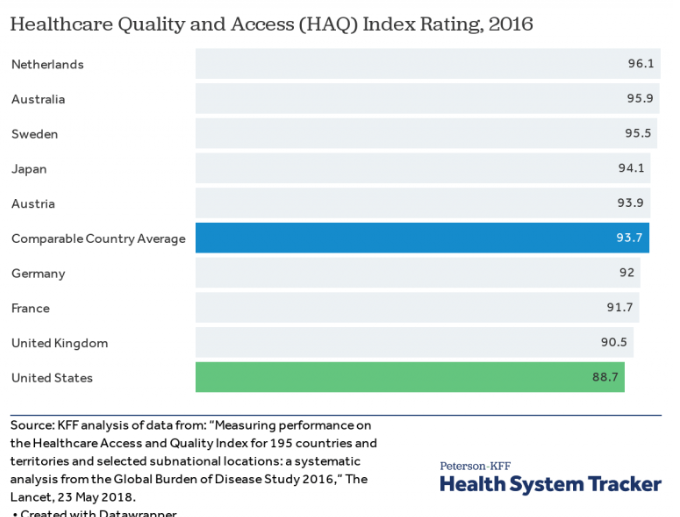
The United States has the highest healthcare cost among comparable countries. However, despite the amount spent on healthcare, the U.S. healthcare system ranks lowest among 11 similar nations in quality of care.
Here are some factors where patient care needs improvement:
Patient Safety and Preventable Medical Errors
According to a 2016 Johns Hopkins study, more than 250,000 deaths yearly in the U.S. are due to medical errors. Additionally, the U.S. ranked last among eight similar countries for amenable mortality or premature death that is preventable with effective and timely care.
Difficulty Finding a Doctor
Currently, patients rely on online reviews and recommendations to find their doctors. However, these methods only sometimes give a holistic perspective on the provider’s knowledge in treating specific conditions. Instead, the reviews are typically limited to staff friendliness and wait times.
This lack of accessible information on credentials, accomplishments, and areas of interest makes it difficult for patients to find the best physician for their specific health concerns.
Patient Experience
The increase in healthcare provider shortages combined with an aging population impacts patient experience. Without the proper workforce to support increased patient volumes, physicians and other providers must see more patients leaving less time per patient encounter.
Limiting time during an appointment can lead to patients not feeling heard or valued, disrespected, and unable to ask questions due to a lack of proper education.
Additionally, physician shortages are causing extensive wait times and reducing access to care in both primary and specialty care.
The overall deterioration of patient experience furthers medical errors, patient compliance, medical inequity, and the overall health of our communities.
5. Provider Shortages
Since the COVID-19 pandemic, healthcare provider shortages have been at an all-time high. Before the pandemic, healthcare workers were already twice as likely to experience burnout. The pandemic only worsened these issues.
According to the annual “Top Issue Confronting Hospitals” survey by the American College of Healthcare Executives, personnel shortages ranked number 1 as hospital CEOs’ top concerns. It is the first time since 2004 that the number one complaint was financial challenges.
Here are some additional statistics on the provider shortage:
- The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects the demand for registered nurses will grow by 9% between 2022 and 2030. That jumps to 45% for nurse practitioners and nurse anesthetists.
- The AAMC estimates the country will have a shortfall of nearly 140,000 physicians by 2033 due to increasing demand.
- According to Health Resources and Service Administration, ninety-six million Americans live in a designated health professional shortage area (HPSA).
- Since the pandemic started to Nov 2021, about 20% of all healthcare workers have quit.
As mentioned, physician shortages directly impact patient outcomes, access to proper healthcare, and overall patient experience. A lack of providers will directly impact public health.
Why is it happening?
There are various reasons for the healthcare worker shortage in the United States. Some of the largest factors are employee satisfaction and burnout.
Burnout
According to U.S. News, 60-75% of clinicians report symptoms of depression, exhaustion, and even sleep disorders, and PTSD since the pandemic. During the pandemic, many physicians and healthcare workers worked longer hours than usual in uncomfortable protective equipment.
Since then, as burnout has increased and the workforce quits, healthcare workers have a greater workload due to an aging population and worker shortages. Additionally, since then, many now face lower reimbursement rates while they try to contain the cost of care.
Before the pandemic, worker burnout costs the country around $4.6 billion annually. It has undoubtedly increased since then. Because of burnout, many health organizations struggle with employee satisfaction and retention.
Employee Satisfaction
Lower compensation rates, increased hours, limited time for patient encounters, higher costs, and increasing administrative duties are some of the factors leading to a deterioration in healthcare worker satisfaction.
Many employees feel undervalued, unheard, and underappreciated for the life-saving work they do daily. These feelings will lead to further employee retention issues.
One Thing You Can Do to Improve Healthcare Today
Of the five challenges facing healthcare this year, there is one each of us can make an impact on, and that is provider shortages. We can ensure our healthcare workers know how much they are appreciated.
Kudoboard is an easy way to gather words of appreciation for healthcare providers and workers. Our boards allow you to create an online thank you card where anyone you invite can contribute their gratitude. The healthcare worker will then receive their card filled with ways their work impacted the lives of their patients, staff, and health organizations.
Taking the time to express your gratitude for the life-saving and preventative measures our healthcare workers do for us can go a long way in helping improve healthcare.